SEH PS105 Bedienungsanleitung
SEH
Druckserver
PS105
Lesen Sie kostenlos die 📖 deutsche Bedienungsanleitung für SEH PS105 (207 Seiten) in der Kategorie Druckserver. Dieser Bedienungsanleitung war für 18 Personen hilfreich und wurde von 2 Benutzern mit durchschnittlich 4.5 Sternen bewertet
Seite 1/207

Print Server
PS Series
User Manual
Windows

Manufacturer:
SEH Computertechnik GmbH
Suedring 11
33647 Bielefeld
Germany
Phone: +49 (0)521 94226-29
Fax: +49 (0)521 94226-99
Support: +49 (0)521 94226-44
Email: info@seh.de
Web: http://www.seh.de
Document:
Type: User Manual
Title: Print Server PS Series Windows
Version: 2.0
Online Links to Important Websites:
Free Guarantee Extension:
Support Contacts & Information:
Sales Contacts & Information:
Downloads:
http://www.seh-technology.com/guarantee
http://www.seh-technology.com/support
http://www.seh-technology.com/sales
http://www.seh-
technology.com/services/downloads.html
InterCon is a registered trademark of SEH Computertechnik GmbH.
SEH Computertechnik GmbH has endeavored to ensure that the information in this documentation is correct. If you detect any
inaccuracies please inform us at the address indicated above. SEH Computertechnik GmbH will not accept any liability for any er
ror or
omission. The information in this manual is subject to change without notification.
All rights are reserved. Copying, other reproduction, or translation without the prior written consent from SEH Computertechnik GmbH is
prohibited.
© 2015 SEH Computertechnik GmbH
All trademarks, registered trademarks, logos and product names are property of their respective owners.

Print Server User Manual Windows i
Contents
1 General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.1 Your Print Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1.2 Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
1.3 Support and Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.4 Your Safety . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.5 First Steps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.6 Finding the Print Server (Determining the IP Address) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Printing in Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 How to Set Up Socket Printing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.2 How to Set Up LPD/LPR Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.3 How to Set Up IPP Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.4 How to Configure Encrypted Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3 Administration Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.1 Administration via Print Server Homepage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.2 Administration Via InterCon-NetTool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.3 Administration via FTP/FTPS Connection . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.4 Administration via Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4 Network Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4.1 How to Configure IPv4 Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4.2 How to Configure IPv6 Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
4.3 How to Adapt the Network Speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
4.4 How to Configure NetBIOS/WINS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.5 How to Configure the DNS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
4.6 How to Configure Bonjour. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
4.7 How to Use SNMP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
4.8 How to Configure POP3 and SMTP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
4.9 How to Configure WLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
5 Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.1 How to Enable PJL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.2 How to Enable 1284.4/MLC. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
5.3 How to Define the Communication Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54

Print Server User Manual Windows ii
5.4 How to Configure COM1 Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
6 Device Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.1 How to Configure the Language of the Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
6.2 How to Configure the Device Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
6.3 How to Determine a Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
7 Print Server Status Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
7.1 How to View Status Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
7.2 What Status Information is Shown? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
7.3 How to Print a Status or Service Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
8 Print Jobs and Print Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
8.1 How to Define a Timeout for Taking on Print Jobs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
8.2 How to Assign Print Jobs Directly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
8.3 How to Modify Print Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
8.4 How to Convert Print Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
8.5 How to Use Logical Printers (Filter Functions) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
9 Printer Status and Printer Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
9.1 How to View the Printer Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
9.2 How to Get Additional Printer Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
9.3 How to Get Printer Messages via Email. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
9.4 How to Get Printer Messages via SNMP Trap . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
9.5 How to View the Job History. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
10 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
10.1 How to Define a Password for the Print Server
(Read/Write Protection) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
10.2 How to Disable the HTTP Access (Protection against Viruses) . . . . . 89
10.3 How to Protect Printers against Unauthorized Access
(IP Sender Control) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
11 Certificate Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
11.1 How to View Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
11.2 How to Create a Self-Signed Certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
11.3 How to Create a Certificate Request for a Requested Certificate. . . 98

Print Server User Manual Windows iii
11.4 How to Save a Requested Certificate in the Print Server. . . . . . . . . . 100
11.5 How to Save a PKCS12 Certificate in the Print Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
11.6 How to Save CA Certificates in the Print Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
11.7 How to Delete Certificates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
12 Network Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
12.1 How to Configure EAP-MD5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
12.2 How to Configure EAP-TLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
12.3 How to Configure EAP-TTLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
12.4 How to Configure PEAP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
12.5 How to Configure EAP-FAST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
13 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
13.1 How to Secure the Print Server Parameters (Backup) . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
13.2 How to Reset Parameters to their Default Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
13.3 How to Perform an Update . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
13.4 How to Restart the Print Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
14 Additional Feature – ThinPrint®. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
14.1 How to Address the Print Server in a ThinPrint Environment . . . . . 136
14.2 How to Define the ThinPrint Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
14.3 How to Define the Bandwidth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
14.4 How to Use ThinPrint AutoConnect. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
14.5 How Does the Print Server Receive Encrypted Data?. . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
15 Additional Feature – Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) . . 141
15.1 How to Create IPsec Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
15.2 How to Use IPsec Configuration Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
15.3 How to Define Exceptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
15.4 How to Enable IPsec Policies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
16 Appendix. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
16.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
16.2 Parameter List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
16.3 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
16.4 List of Figures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
16.5 Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198

General Information
Print Server User Manual Windows 1
1 General Information
What Information
Do You Need?
• ’Your Print Server’ 1
• ’Documentation’ 2
• ’Support and Service’ 4
• ’Your Safety’ 5
• ’First Steps’ 6
• ’Finding the Print Server (Determining the IP Address)’ 6
1.1 Your Print Server
Purpose Print servers are active network components that receive print jobs
from connected users or user groups within a network and forward
them to printers or other end devices.
Supported Systems Print servers have been designed for the use in the following sys-
tems:
• Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10
• Mac OS X 10.8.x, Mac OS X 10.9.x, Mac OS X 10.10.x
This document describes the usage in Windows environments. Infor-
mation about the usage in other environments can be found in the
relevant system-specific User Manual. For further information; see:
’Documentation’ 2.
This chapter contains information concerning the
device and the documentation as well as notes about
your safety. You will learn how to benefit from your
print server and how to operate the device properly.

General Information
Print Server User Manual Windows 2
1.2 Documentation
Structure of the
Documentation
The print server documentation consists of the following docu-
ments:
Scope and Content This documentation describes a variety of print server models. This
means that features will be described that may not be applicable to
your print server. Information about the features of your print
server can be found in the data sheet of your print server model.
Due to the multitude of supported operating systems, instructions
are described exemplarily. The respective concept can be transferred
to other versions of the operating system.
Document Features This documentation has been designed as an electronic document
for screen use. Many programs (e.g. Adobe® Reader®) offer a book-
mark navigation feature that allows you to view the entire docu-
ment structure.
This document contains hyperlinks to the associated information
units. If you want to print this documentation, we recommend using
the printer setting 'Duplex' or 'Booklet'.
Terminology Used in
this Document
The explanation of technical terms used in this document is summa-
rized in a glossary. The glossary provides a quick overview of techni-
cal matters and background information; see: 159.
User Manual
Detailed description of the print server installation,
configuration, and administration. System-specific
instructions for the following systems:
- Windows
- Mac
Quick Installation Guide
Information about security, hardware installation, and the
initial operation procedure.
PDF
Printed
PDF

General Information
Print Server User Manual Windows 3
Symbols and
Conventions
A variety of symbols are used within this document. Their meaning is
listed in the following table:
Table 1: Conventions within the documentation
Symbol / Convention Description
Warning
A warning contains important information that
must be heeded. Non-observance may lead to
malfunctions.
Note
A notice contains information that should be
heeded.
Proceed as follows:
1. Select…
The ‘hand’ symbol marks the beginning of
instructions. Individual instructions are set in
italics.
Confirmation The arrow confirms the consequence of an
action.
Requirements Hooks mark requirements that must be met
before you can begin the action.
Option A square marks procedures and options that
you can choose.
• Eye-catchers mark lists.
This sign indicates the summary of a chapter.
The arrow marks a reference to a page within
this document. In the PDF file, you can jump to
this page by clicking the symbol.
Bold Established terms (of buttons or menu items, for
example) are set in bold.
Courier Command lines are set in 'Courier' font.
'Proper names' Proper names are put in inverted commas.

General Information
Print Server User Manual Windows 4
1.3 Support and Service
Support SEH Computertechnik GmbH offers extensive Support. If you have
any questions, please contact our hotline.
Downloads Downloads can be found on the SEH Computertechnik GmbH home-
page:
http://www.seh-technology.com/services/downloads.html
For print servers you will find:
• current firmware/software
• current tools
• current documentation
• current product information
• product data sheets
• and much more
Monday – Thursday
Friday
8:00 a.m. – 4:45 p.m.
8:00 a.m. – 15:15 p.m.
+49 (0)521 94226-44
support@seh.de
http://www.seh.de/

General Information
Print Server User Manual Windows 5
1.4 Your Safety
Read and observe all safety regulations and warnings found in the
documentation, on the device and on the packaging. This will avoid
potential misuse and prevent damages to people and devices.
SEH Computertechnik GmbH will not accept any liability for per-
sonal injuries, property damages and consequential damages result-
ing from the non-observance of the mentioned safety regulations
and warnings. SEH Computertechnik GmbH will not accept any lia-
bility for loss of data, property damages and consequential damages
resulting from the non-observance of the mentioned safety regula-
tions and warnings.
Intended Use Print servers are network interfaces for printers. They are designed
for the direct integration of printers into networks. The print server
has been designed for use in office environments.
Improper Use All uses of the device that do not comply with the print server func-
tionalities described in the documentation are regarded as improper
uses. It is not allowed to make modifications to the hardware and
software or to try to repair the device.
Safety Regulations Before starting the initial operation procedure of the print server,
please note the safety regulations in the 'Quick Installation Guide'.
This document is enclosed in the packaging in printed form.
Warnings Read and observe all warnings mentioned in this document. Warn-
ings are found before any instructions known to be dangerous. They
are presented as follows:
Warning!

General Information
Print Server User Manual Windows 6
1.5 First Steps
This section provides all the information that you need for a fast
operational readiness.
Proceed as follows:
1. Read and observe the security regulations in order to avoid
damages to people and devices; see:
5
.
2. Carry out the hardware installation. The hardware installation
comprises the connection of the ISD to the network and the
mains supply; see: 'Quick Installation Guide'.
3. Make sure that the print server has an IP configuration which is
suitable for your network; see:
6
.
4. Configure your clients for printing via the print server, see:
9
.
Via the print server you can print to the printers connected.
1.6 Finding the Print Server (Determining the IP
Address)
Why IP Addresses? An IP address is used to address network devices in an IP network.
TCP/IP network protocols require the storing of the IP configuration
in the print server so that the device can be addressed within the
network.
How Does the Print
Server Obtain Its IP
Configuration?
SEH print servers are shipped without IP configuration. Once the
print server is connected to the network, it automatically receives an
IP configuration via the boot protocols BOOTP or DHCP. If this is not
the case, the print servers seeks a ZeroConf IP address from the
ZeroConf address range (169.254.0.0/16).
How to Find The
Print Server in the
Network
(Determining the IP
Address)
The InterCon-NetTool is a software tool developed by SEH Comput-
ertechnik GmbH for the administration of SEH print servers. By
means of this tool you can find the print server's IP address, as
described below.
The client, printer and print server must be assigned to the same
local network segment for the initial configuration.
Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 8
2 Printing in Windows
The print server embeds non-network-ready printers into the net-
work. In order to print via the print server, the printers connected to
the print server must be set up as printers on the client system. This
is done via the Windows settings.
The following descriptions show how printers are set up in Windows
10. The menu navigation in other Windows systems may vary. For
more information, please read the printer setup instructions in your
Windows user manual.
What Information
Do You Need?
• ’How to Set Up Socket Printing’ 9
• ’How to Set Up LPD/LPR Printing’ 11
• ’How to Set Up IPP Printing’ 14
• ’How to Configure Encrypted Printing’ 16
This chapter describes printing via the print server in
Windows.

Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 9
2.1 How to Set Up Socket Printing
Socket printing is carried out by means of direct TCP/IP ports.
Procedure Follow these steps if you want to print:
• ’Setting up the Printer on the Client’ 9
• ’Configuring the Printer Port’ 10
Setting up the Printer on the Client
The print server is connected to the network and the printer;
see: Quick Installation Guide.
The print server and the printer are turned on.
The print server has a suitable IP configuration, see: 7.
You know the print server's current IP address; see: 7.
Proceed as follows:
1. Open the Start menu.
2. Select Settings.
The Settings dialog appears.
3. Select Devices.
The Add printers & scanners dialog appears.
4. Select Add a printers or scanners.
Printers and scanners are searched for.
5. Scroll down to the end of the result list and select The printer
that I want isn't listed.
The Add printer dialog appears.
6. Tick Add a local printer or network printer with manual
settings.
7. Tick Create a new port.
8. From the list Type of port, select Standard TCP/IP Port.
9. Click Next.
10. In the Hostname or IP address box, enter the IP address of the
print server.
Omit leading zeros from the IP address!

Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 11
4. From the shortcut menu, select Printer properties.
The Properties dialog appears.
5. Select the Ports tab.
6. In the list, select the port.
7. Click Configure.
The Configure Standard TCP/IP Port Monitor dialog appears.
8. In the Protocol area, tick the option Raw.
9. In the Raw Settings area, define the Port Number.
10. Untick SNMP Status Enabled.
11. Click OK to confirm.
The settings will be saved.
2.2 How to Set Up LPD/LPR Printing
When using the printing protocol Line Printer Daemon/Line Printer
Remote-Protokoll (LPD/LPR) , printing is done via a TCP/IP connec-
tion.
Mode of Operation LPD/LPR consists of two components:
• Line Printer Daemon (LPD) refers to the process which receives
print jobs from the LPR client. LPD runs on the print server. Thus
the print server is called LPD server.
• Line Printer Remote (LPR) is the term for the process which
sends print jobs to a printer or respectively to a print queue. The
client (PC, etc.) which sends the print job is the LPR client and
must be equipped with the required software.
Procedure Follow these steps if you want to print:
• ’Activating LPR on the Client’ 12.
• ’Setting up the Printer on the Client’ 12.
• ’Setting Up the Printer Port’ 13.

Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 12
Activating LPR on the Client
Proceed as follows:
1. In the taskbar, enter 'Programs and Features' into the search
box.
The search results are displayed.
2. In the search results, select Programs and Features.
The Programs and Features dialog appears.
3. Select Turn Windows features on or off.
The Windows Features dialog appears.
4. Under Print and Document Services activate LPR Port Monitor.
5. Click OK to confirm.
LPR is activated on the client.
Setting up the Printer on the Client
Requirements The print server is connected to the network and the printer;
see: Quick Installation Guide.
The print server and the printer are turned on.
The print server has a suitable IP configuration, see: 7.
You know the print server's current IP address; see: 7.
Proceed as follows:
1. Open the Start menu.
2. Select Settings.
The Settings dialog appears.
3. Select Devices.
The Add printers & scanners dialog appears.
4. Select Add a printers or scanners.
Printers and scanners are searched for.
5. Scroll down to the end of the result list and select The printer
that I want isn't listed.
The Add printer dialog appears.
6. Tick Create a new port.
7. From the list Type of port, select Standard TCP/IP Port.

Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 13
8. Into the Address box, enter the IP address of the print server.
Omit leading zeros from the IP address!
9. Enter a description into the Port name box.
10. Untick Query the printer and automatically select the driver to
use.
11. Click Next.
12. (In the area Device Type, tick Standard.)
13. (Select Generic Network Card from the list.)
14. (Click Next.)
15. From the list Manufacturer and Printers, select the printer
model.
16. Click Next.
17. Enter a description into the Printer name box.
18. Click Next.
The printer is being installed.
19. Click Print a test page.
The test page is printed.
20. Click Finish.
The printer is set up on the client. Set up the printer port for
LPD/LPR printing13.
Setting Up the Printer Port
Proceed as follows:
1. In the taskbar, enter 'Devices and Printers' into the search box.
The search results are displayed.
2. In the search results, select Devices and Printers.
The Devices and Printers dialog appears.
3. In the list, select the printer.
4. From the shortcut menu, select Printer properties.
The Properties dialog appears.
5. Select the Ports tab.
6. In the list, select the port.

Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 14
7. Click Configure.
The Configure Standard TCP/IP Port Monitor dialog appears.
8. In the list, select the port.
9. Click Configure.
10. The Configure Standard TCP/IP Port Monitor dialog appears.
11. In the Protocol area, tick the option LPR.
12. Into the Queue Name box, enter a logical
printer (lp1 - lp8).
The logical printer defines the printer port to which the print data is sent. This is
relevant for print server models with several physical printer ports (COM1, USB1,
etc.). If no logical printer is defined, the logical printer no. 1 will be used
automatically. For further information; see:
68.
13. Untick SNMP Status Enabled.
14. Click OK to confirm.
The settings will be saved. If you print via the printer you have
set up, the print job will be printed on the printer connected to
the print server.
2.3 How to Set Up IPP Printing
In IPP (Internet Printing Protocol) the print data is transmitted via
HTTP to the printer. When printing via IPP, the print server is
addressed via a Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). The syntax of the
URI looks as follows:
http://<IP address>:631/ipp/<logical printer>
Requirements The print server is connected to the network and the printer;
see: Quick Installation Guide.
The print server and the printer are turned on.
The print server has a suitable IP configuration, see: 7.
You know the print server's current IP address; see: 7.
Proceed as follows:
1. Open the Start menu.
2. Select Settings.
The Settings dialog appears.
3. Select Devices.
The Add printers & scanners dialog appears.

Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 15
4. Select Add a printers or scanners.
Printers and scanners are searched for.
5. Scroll down to the end of the result list and select The printer
that I want isn't listed.
The Add printer dialog appears.
6. Tick Select a shared printer by name.
7. Into the Select a shared printer by name box, enter the print
server's IP address and the socket number for IPP printing. If
necessary, enter the name of the logical printer (lp1–lp8):
http://<IP address>:631/ipp/<logical printer>
With print server models with several physical ports, the logical printer is also
used to address the port. If no name or an incorrect name has been entered, the
print data is automatically routed to the printer through logical printer no.1. For
further information; see:
68.
Omit leading zeros from the IP address!
8. Click Next.
The Add Printer Wizard appears.
9. From the list Manufacturer and Printers, select the printer
model.
10. To confirm click OK.
The printer is being installed.
11. Click Next.
12. Print a test page.
13. Click Finish.
The printer is set up on the client. If you print via the printer you
have set up, the print job will be printed on the printer
connected to the print server.

Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 16
2.4 How to Configure Encrypted Printing
You can encrypt the print data that is sent to the print server from
the client.
Mode of Operation The communication between client and print server is encrypted via
SSL/TLS. In this process, the print server is addressed via a Uniform
Resource Identifier (URI). The syntax of the URI looks as follows:
https://<IP address>:443/ipp/<logical printer>
For authentication a print server certificate is required. The 'Com-
mon name' box of the print server certificate must contain the print
server's IP address.
Procedure In order to encrypted printing, proceed as follows:
• Create a self-signed certificate in the print server. Into the
'Common name' box, enter the IP address of the print server.
Omit leading zeros from the IP address. See: ’Wie erstelle ich ein
selbstsigniertes Zertifikat?’ 92.
• Save the print server certificate on the client from which you
want to print; see: 16.
• On the client, create a printer for the printer connected to the
print server; see: 18.
You must observe the following instructions in the indicated order.
If this procedure is not adhered to, the printer connected to the
print server cannot be set up as printer on the client.
Saving the Print Server Certificate on the Client
The print server certificate can be saved on the client via the Inter-
net Explorer.
Requirements You have administrative rights on the client.
The Internet Explorer is installed on the client. (It is installed by
default in Windows 10.)

Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 17
Proceed as follows:
1. In the taskbar, enter 'Internet Explorer' into the search box.
The search results are displayed.
2. In the search results, right click on Internet Explorer.
The context menu appears.
3. Select Run as administrator.
A security query appears.
4. Confirm the security query by clicking Yes.
The Internet Explorer starts.
5. Open an encrypted connection to the print server: To do this,
enter 'https://' and the IP address of the print server as the URL.
Example: https://10.168.1.234
The following message appears: There is a problem with this
website's security certificate.
6. Click Continue to this website (not recommended).
The Print Server Homepage appears. The address bar is red and
shows a certificate warning.
7. In the address bar, click Certificate error.
The popup Untrusted Certificate appears.
8. Click View certificates.
The Certificate dialog appears.
9. Click Install Certificate.
The Certificate Import Wizard appears.
10. Select Local Machine.
11. Click Next.
12. Select Place all certificates in the following store.
13. Click Browse.
The Select Certificate Store dialog appears.
14. From the list, select Trusted Root Certification Authorities.
15. Click OK to confirm.
In the Select Certificate Store dialog, the folder Trusted Root
Certification Authorities is displayed in the Certificate store
box.
16. Click Next.
17. Click Finish.
A success message appears.
Printing in Windows
Printserver User Manual Windows 18
18. Confirm the success notification by clicking OK.
19. Close the certificate dialog by clicking OK.
The print server certificate is installed on the client.
Setting up the Printer on the Client
Requirements The print server is connected to the network and the printer;
see: Quick Installation Guide.
The print server and the printer are turned on.
The print server has a suitable IP configuration, see: 7.
You know the print server's current IP address; see: 7.
Proceed as follows:
1. Open the Start menu.
2. Select Settings.
The Settings dialog appears.
3. Select Devices.
The Add printers & scanners dialog appears.
4. Select Add a printers or scanners.
Printers and scanners are searched for.
5. Scroll down to the end of the result list and select The printer
that I want isn't listed.
The Add printer dialog appears.
6. Tick Select a shared printer by name.
7. Into the Select a shared printer by name box, enter the print
server's IP address and the socket number for IPP printing. If
necessary, enter the name of the logical printer (lp1–lp8):
https://<IP address>:443/ipp/<logical printer>
With print server models with several physical ports, the logical printer is also
used to address the port. If no name or an incorrect name has been entered, the
print data is automatically routed to the printer through logical printer no.1. For
further information; see:
68.
In the URI, enter the IP address exactly as it is written in the file
'Common name' of the print server certificate. Omit leading zeros
in both cases. Otherwise the print server cannot be addressed.

Administration Methods
Print Server User Manual Windows 21
3.1 Administration via Print Server Homepage
Functionalities The print server has a user interface, the Print Server Homepage,
which can be opened in an Internet browser (Internet Explorer,
Mozilla Firefox, Safari).
The print server can be configured and monitored via the Print
Server-Homepage.
Requirements The print server is connected to the network, printer and the
mains voltage.
The print server has a suitable IP configuration, see: 7.
Starting the Print
Server Homepage
Proceed as follows:
1. Open your browser.
2. Enter the IP address of the print server as the URL.
The Print Server Homepage is displayed in the browser.
If the Print Server Homepage is not displayed, check the proxy set-
tings of your browser.
You can also start the Print Server Homepage via the software tool
'InterCon-NetTool'.
Proceed as follows:
1. Select the print server in the device list.
2. Select Actions – Launch Browser from the menu bar.
The Print Server Homepage is displayed in the browser.
Administration Methods
Print Server User Manual Windows 23
3.2 Administration Via InterCon-NetTool
The InterCon-NetTool is a software tool developed by SEH Comput-
ertechnik GmbH for the administration of SEH print servers.
Mode of Operation After the InterCon-NetTools is started, the network will be scanned
for connected print servers. The network range to be scanned is
freely definable. All print server found will be displayed in the
'device list'.
You can modify the device list and adapt it to your individual needs.
You can select the print servers in the device list and configure
them.
Installation In order to use the InterCon-NetTool, the program must be installed
on a computer with Windows operating system.
Proceed as follows:
1. Download the installation file for the InterCon-NetTool from
the homepage of the SEH Computertechnik GmbH:
http://www.seh-technology.com/services/downloads.html
2. Start the installation file.
3. Select the desired language.
4. Follow the installation routine.
The InterCon-NetTool will be installed on your client.
Program Start You can identify the InterCon-NetTool by its icon: . The Inter-
Con-NetTool can be started with the usual mechanisms of your
operating system.
The program settings are saved in the InterCon-NetTool.ini' file. This
file is stored in the user folder of the user that is currently logged in.

Administration Methods
Print Server User Manual Windows 24
InterCon-NetTool
Structure
After the program start you will see the main dialog with the fol-
lowing elements. The dialog may vary, depending on which elements
you have chosen to be shown or hidden.
Fig. 2: InterCon-NetTool - Main dialog
Which Functions
Are Supported?
The InterCon-NetTool allows you to
• ’assign an IPv4 configuration to the print server’ 7
• ’restart the print server’ 133
• ’reset the print server parameters to their default settings’ 122
• ’start the Print Server-Homepage’ 21
• ’carry out updates’ 133
• ’save and transfer the print server parameters’ 118
• ’switch from the BIOS mode to the default mode’ 195
Detailed information on how to use the InterCon-NetTool can be
found in the Online Help. To start the Online Help, select Help –
Online Help from the menu bar.
ToolbarMenu bar Device list
Filter for the device list Shortcut menu

Administration Methods
Print Server User Manual Windows 25
3.3 Administration via FTP/FTPS Connection
FTP The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) allows the exchange of data between
the print server and an FTP client in TCP/IP networks.
FTP over SSL/TLS
(FTPS)
The print server also supports FTPS (FTP over SSL) for a safe data
interchange between the print server and the client.
We recommend using SSL/TLS so that unencrypted user names, pass-
words, and data cannot be read by unauthorized persons.
Configuring
Parameters via FTP
Connection
You can configure all print server parameters via FTP. To this pur-
pose, you must download the 'parameters' file to your local com-
puter via FTP and then edit it.
Proceed as follows:
1. Change to the directory in which you wish to save the file.
2. Open an FTP connection to the print server:
Syntax: ftp <IP address>
Example: ftp 192.168.0.123
3. Enter an arbitrary user name.
4. Enter the print server password or press the enter key if no
password has been assigned.
5. Transfer the 'parameters' file from the print server to your local
computer:
get parameters
6. Edit the file using a text editor.
The syntax and values can be obtained from the parameter list;
see:
162
.
7. Send the file back to the print server:
put parameters
8. Close the FTP connection:
quit
The print server will be configured using the new values.

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 31
4 Network Settings
What Information
Do You Need?
• ’How to Configure IPv4 Parameters’ 31
• ’How to Configure IPv6 Parameters’ 34
• ’How to Adapt the Network Speed’ 37
• ’How to Configure NetBIOS/WINS’ 38
• ’How to Configure the DNS’ 40
• ’How to Configure Bonjour’ 41
• ’How to Use SNMP’ 43
• ’How to Configure POP3 and SMTP’ 43
• ’How to Configure WLAN’ 47
4.1 How to Configure IPv4 Parameters
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol over Internet Protocol) for-
wards data packets across several connections and establishes a con-
nection between the network participants.
The boot protocols DHCP and BOOTP belong to the TCP/IP protocol
family. You can define various IPv4 parameters for an ideal integra-
tion of your print server into a TCP/IP network. For further informa-
tion about the IP configuration, see: 7.
What do you want
to do?
’Configuring IPv4 Parameters via the Print Server Homepage’
32
’Configuring IPv4 Parameters via the InterCon-NetTool’ 33
You can define various settings for an ideal integration
of the print server into a network. This chapter explains
which network protocols and settings are supported by
the print server.

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 32
Configuring IPv4 Parameters via the Print Server Homepage
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the Print Server Homepage.
2. Select Configuration – TCP/IP.
3. Configure the TCP/IP parameters; see: Table 2
32
.
4. Click Save to confirm.
The settings are saved.
Table 2: TCP/IP Parameters
Parameters Description
IP address IP address of the print server
Subnet Mask Subnet mask of the print server
Gateway Gateway address of the print server
Multicast router as gateway If this parameter has been enabled, it will be
attempted to automatically enter the address of the
found multicast router as gateway address.
If disabled, the gateway address has to be entered
manually.
Host name Host Name of the print server
Contact person Freely definable description
Location Freely definable description
DHCP
BOOTP
ZeroConf
Enables/disables the protocols 'DHCP', 'BOOTP',
and 'ZeroConf'.
Protocols offer various possibilities to save the IP
address in the print server.
We recommend disabling these options once an IP
address has been assigned to the print server.
Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 33
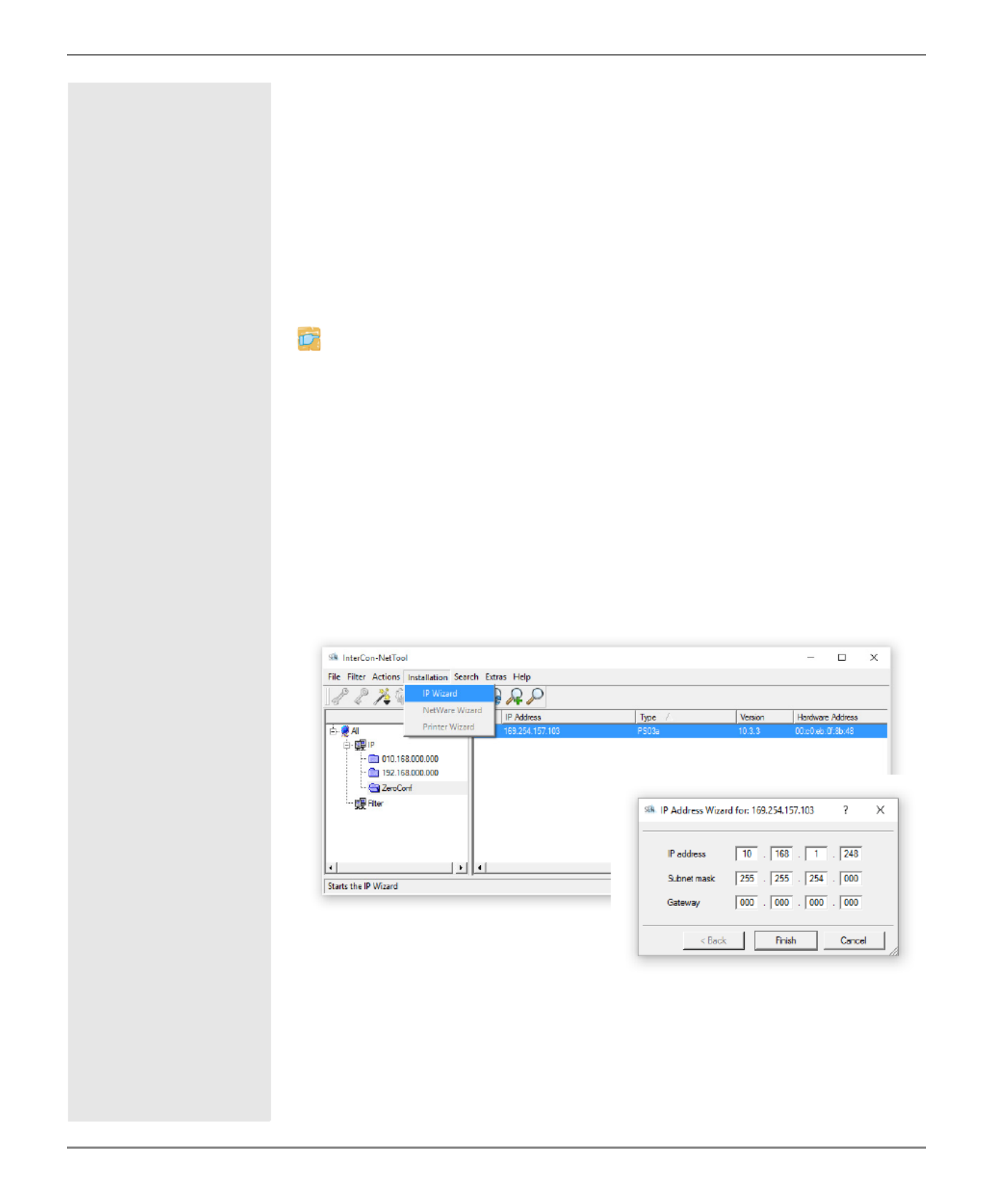
Configuring IPv4 Parameters via the InterCon-NetTool
Wizards facilitate the installation and configuration of print servers
via the InterCon-NetTool. You can easily enter the desired IP config-
uration and save it in the print server using the IP Wizard.
Requirements The InterCon-NetTool is installed on the client, see: 15.
The network scan via Multicast has been enabled in the
InterCon-NetTool.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the InterCon-NetTool.
2. Select the print server in the device list.
The print server is displayed in the device list under the filter 'ZeroConf' with an
IP address from the address range (169.254.0.0/16) which is reserved for
ZeroConf.
3. Select Installation – IP Wizard.
The IP Wizard is started.
4. Follow the instructions of the Wizard.
The settings are saved.
Fig. 5: InterCon-NetTool - IP Wizard

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 34
4.2 How to Configure IPv6 Parameters
You can integrate the print server into an IPv6 network.
What Are the
Advantages of IPv6?
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6) is the successor of the more com-
mon IPv4. Both protocols are standards for the network layer of the
OSI model and regulate the addressing and routing of data packets
via a network. The introduction of IPv6 has many benefits:
• IPv6 increases the IP address space from 232 (IPv4) to 2128 (IPv6)
IP addresses
• Auto Configuration and Renumbering
• Efficiency increase during routing due to reduced header
information.
• Integrated services such as IPSec, QoS, Multicast
• Mobile IP
What is the Structure
of an IPv6 Address?
An IPv6 address consists of 128 bits. The normal format of an IPv6
address is eight fields. Each field contains four hexadecimal digits
representing 16 bits.
Each field is separated by a colon (:).
Example: fe80 : 0000 : 0000 : 0000 : 0000 : 10 : 1000 :
1a4
Leading zeros in a field can be omitted.
Example: fe80 : 0 : 0 : 0 : 0 : 10 : 1000 :
1a4
An IPv6 address may be entered or displayed using a shortened ver-
sion when successive fields contain all zeros (0). In this case, two
colons (::) are used. However, the use of two colons can be used only
once in an address.
Example: fe80 : : 10 : 1000 : 1a4
As a URL in a Web browser, an IPv6 address must be enclosed in
brackets. This prevents port numbers from being mistakenly
regarded as part of an IPv6 address.
Example: http://[2001:608:af:1::100]:443

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 35
The URL will only be accepted by browsers that support IPv6.
Which Types of IPv6
Addresses Are
Available?
There are different types of IPv6 addresses. The prefixes of the IPv6
addresses provide information about the IPv6 address types.
• Unicast addresses can be routed globally. These addresses are
unique and therefore unambiguous. A packet that is sent to a
unicast address will only arrive to the interface that is assigned
to this address. Unicast addresses have the prefixes '2' or '3'.
• Anycast addresses are assigned to more than one interface. This
means that a data packet that is sent to this address will arrive
at various devices. The syntax of anycast addresses is the same as
the one of unicast addresses. The difference is that anycast
addresses choose one interface out of many.
A packet that is dedicated to an anycast address arrives at the
nearest interface (in line with the router metrics). Anycast
addresses are only used by routers.
• Multicast addresses allow you to send data packets to different
interfaces at the same time without a proportional increase of
the bandwidth. A multicast address can be recognized by the
prefix 'ff'.
What do you want
to do?
’Configuring IPv6 Settings via the Print Server Homepage’
35
’Configuring Logical Printers via the InterCon-NetTool’ 36
'View IPv6 status' 55
Configuring IPv6 Settings via
the Print Se
rver Homepage
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the Print Server Homepage.
2. Click Configuration – IPv6.
3. Configure the IPv6 parameters; see: Table 3
36
.
4. Click Save to confirm.
The settings are saved.
Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 36
Table 3: IPv6 Parameters
Configuring Logical Printers via the InterCon-NetTool
Requirements The InterCon-NetTool is installed on the client, see: 15.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the InterCon-NetTool.
2. Double-click the print server in the device list.
The Settings dialog appears.
3. Click Configuration – IPv6.
4. Configure the IPv6 parameters; see: Table 3
36
.
5. Click OK to confirm.
The settings are saved.
Parameters Description
IPv6 Enables/disables the IPv6 functionality of the print server.
IPv6 address Defines a print server IPv6 unicast address assigned
manually in the format n:n:n:n:n:n:n:n.
Every 'n' represents the hexadecimal value of one of the
eight 16 bit elements of the address. An IPv6 address may
be entered or displayed using a shortened version when
successive fields contain all zeros (0). In this case, two
colons (::) are used.
Router Defines the IPv6 unicast address of the router. The print
server sends its 'Router Solicitations' (RS) to this router.
Prefix length Defines the length of the subnet prefix for the IPv6 address.
The value 64 is preset.
Address ranges are indicated by prefixes. The prefix length
(number of bits used) is added to the IPv6 address and
specified as a decimal number. The decimal number is
separated by '/'.
Automatic configuration Enables/disables the automatic assignment of the IPv6
address for the print server.
Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 37
4.3 How to Adapt the Network Speed
Network communication is done via three direction-oriented trans-
mission methods between two equal data stations. Simplex, half
duplex and full duplex.
Duplex Mode The print server is able to recognize the duplex mode used in the
Ethernet and to automatically adjust to it.
The 'Auto' mode is preset. There is also the possibility to manually
adjust the setting of the desired duplex mode.
If you set the speed manually, the speed must correspond to the
speed of the other network components. It is not possible to
operate the print server with full duplex if the hub functions with
half duplex, for example.
What do you want
to do?
’Adapting the Speed via the Print Server Homepage’ 37
’Adapting the Speed via InterCon-NetTool’ 37
Adapting the Speed via the Print Server Homepage
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the Printserver Homepage.
2. Select Configuration – General.
3. Select the desired setting from the Ethernet settings list.
4. Click Save to confirm.
The setting will be saved.
Adapting the Speed via InterCon-NetTool
Requirements The InterCon-NetTool is installed on the client, see: 15.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the InterCon-NetTool.
2. Double-click the print server in the device list.
The Properties dialog appears.

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 38
3. Select Configuration – General.
4. Select the desired setting from the Ethernet settings list.
5. Click OK to confirm.
The setting will be saved.
4.4 How to Configure NetBIOS/WINS
'NetBIOS' (Network Basic Input Output System) allows you to
address a client in Microsoft Windows networks not only via a
unique TCP/IP address but also via a unique NetBIOS name.
Benefits and
Purpose
'WINS' (Windows Internet Naming Service) is a system for the
dynamic resolution of NetBIOS names.
What Do You Want to
Do?
’Configuring NetBIOS/WINS via the Printserver Homepage’
38
’Configuring NetBIOS/WINS via InterCon-NetTool’ 39
Configuring NetBIOS/WINS via the Printserver Homepage
Requirements A WINS server is available in the network.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the Printserver Homepage.
2. Select Configuration - Microsoft Windows.
3. Configure the parameters; see: Table 4
38
.
4. Click Save to confirm.
The settings are saved.
Table 4: Microsoft Windows Parameters
Parameters Description
NetBIOS Enables/disables peer-to-peer printing.
NetBIOS name Print Server name Appears in the relevant
workgroup or domain.
NetBIOS domain Name of an existing workgroup or domain.

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 39
Configuring NetBIOS/WINS via InterCon-NetTool
Requirements The InterCon-NetTool is installed on the client, see: 15.
A WINS server is available in the network.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the InterCon-NetTool.
2. Double-click the print server in the device list.
The Properties dialog appears.
3. Select Configuration - Microsoft Windows.
4. Configure the parameters; see: Table 4
38
.
5. Click OK to confirm.
The settings are saved.
NetBIOS refresh every Time interval (in minutes) for updating the NetBIOS
parameters.
WINS registration Enables/disables the WINS services.
WINS via DHCP Enables/disables the entry of the IP address of a
WINS server via DHCP.
If the option is disabled, you can enter the IP address
of the WINS server manually.
Primary WINS server IP address of the primary WINS server
Secondary DNS server IP address of the secondary WINS server
Parameters Description

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 41
Configuring DNS via the InterCon-NetTool
Requirements The InterCon-NetTool is installed on the client, see: 15.
A WINS server is available in the network.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the InterCon-NetTool.
2. Double-click the print server in the device list.
The Properties dialog appears.
3. Select Configuration – DNS.
4. Configure the DNS parameters; see: Table 5
40
.
5. Click OK to confirm.
The settings are saved.
4.6 How to Configure Bonjour
'Bonjour' allows the automatic recognition of computers, devices,
and network services in TCP/IP-based networks.
The print server uses Bonjour to:
• check the IP address assigned via ZeroConf (7).
• match host names and IP addresses
• announce its Bonjour services (printing services, Printserver
Homepage)
What do you want
to do?
’Configuring Bonjour via the Print Server Homepage’ 41
’Configuring Bonjour via the InterCon-NetTool’ 42
'View Bonjour status' 55
Configuring Bonjour via the Print Server Homepage
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the Printserver Homepage.
2. Select Configuration – Bonjour.

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 42
3. Configure the Bonjour parameters; see: Table 6
42
.
4. Click Save to confirm.
The settings are saved.
Table 6: Bonjour Parameters
Configuring Bonjour via the InterCon-NetTool
Requirements The InterCon-NetTool is installed on the client, see: 15.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the InterCon-NetTool.
2. Double-click the print server in the device list.
The Properties dialog appears.
3. Select Configuration – Bonjour.
4. Configure the Bonjour parameters; see: Table 6
42
.
5. Click OK to confirm.
The settings are saved.
Parameters Description
Bonjour Enables/disables Bonjour.
Bonjour name
(LPT1,LPT2...)
(USB1,USB2...)
Defines the Bonjour name of the print server.
The print server uses this name for its Bonjour
services. If no Bonjour name is entered, the default
name will be used (printer name@ICxxxxxx).
You can enter a maximum of 63 characters. The
name must not start with an underscore.
(As for print servers with several physical printer
ports, each port can have a name).

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 43
4.7 How to Use SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) has become the
standard protocol for the administration and monitoring of network
elements. The protocol controls communication between the moni-
tored devices and the monitoring station.
SNMP allows you to read and edit management information pro-
vided by the network elements. The collection of management
information of a device is called MIB.
Private MIB of the
Print Server
The print server provides the standard 'MIB-II' and a 'private MIB'
(Management Information Base). All print server parameters and
status information are saved in the 'private MIB'. The 'private MIB' is
saved in the print server on delivery and can be installed immedi-
ately.
Benefits and
Purpose
The print server parameters can be queried and configured by a
management tool by means of the SNMP protocol.
Requirements The print server is connected to the network and the printer.
The print server is known to the network via its IP address, see:
7.
For more information, read the manual of your SNMP management
tool.
4.8 How to Configure POP3 and SMTP
You must configure the protocols POP3 and SMTP on the TPR so that
the notification service (77) and the administration via email
(19) will work properly.
POP3 'POP3' (Post Office Protocol Version 3) is a transfer protocol that a
client can use to fetch emails from a mail server. POP3 is used in
print servers to administer print servers via email; see: 19.
SMTP 'SMTP' (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is a protocol that controls the
sending of emails in networks. SMTP is used in print servers to

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 44
administer print servers via email (see: 19) and to send printer
information via email (see: 77).
What Do You Want to
Do?
’Configuring POP3 via the Print Server Homepage’ 44
’Configuring POP3 via the InterCon-NetTool’ 45
’Configuring SMTP via the Printserver Homepage konfigurieren’
45
’Configuring SMTP via the InterCon-NetTool’ 47
'View POP3/SMTP status'55
Configuring POP3 via the Print Server Homepage
Requirements The print server is set up as user with its own email address on a
POP3 server.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the Printserver Homepage.
2. Select Configuration – Mail.
3. Configure the POP3 parameters; see: Table 7
44
.
4. Click Save to confirm.
The settings are saved.
Table 7: POP3 Parameters
Parameters Description
POP3 Enables/disables the POP3 functionality.
Server name Defines the POP3 server via the IP address or the
host name.
The host name can only be used if a DNS server was
configured beforehand.
User name Defines the user name used by the print server to log
on to the POP3 server.
Security Defines the authentication method
(APOP/SSL/TLS).
Check mail every Defines the time interval (in minutes) for retrieving
emails from the POP3 server.

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 45
Configuring POP3 via the InterCon-NetTool
Requirements The InterCon-NetTool is installed on the client, see: 15.
The print server is set up as user with its own email address on a
POP3 server.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the InterCon-NetTool.
2. Double-click the print server in the device list.
The Properties dialog appears.
3. Select Configuration - Mail - POP3.
4. Configure the POP3 parameters; see: Table 7
44
.
5. Click OK to confirm.
The settings are saved.
Configuring SMTP via the Printserver Homepage konfigurieren
Requirements The print server is set up as user with its own email address on a
POP3 server.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the Print Server Homepage.
2. Select Configuration - Mail - SMTP.
Server port Defines the port used by the print server for receiving
emails. The port number 110 is preset. When using
SSL/TLS, enter 995 as port number.
Password Defines the password used by the print server to log
on to the POP3 server.
Delete read messages Enables/disables the automatic deletion of read
emails.
Ignore mail exceeding Defines the maximum email size (in KByte) to be
accepted by the print server.
(0 = unlimited)
Parameters Description

Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 49
is regenerated periodically. The WPA mechanism requires an authen-
tication at the beginning of a connection.
In the 'Personal Mode' authentication is done via the Pre Shared Key
(PSK). The PSK is a password with 8–63 alphanumerical characters.
The 'Enterprise Mode' uses the EAP authentication method.
An individual 128 bit key is used for data encryption after the
authentication. The encryption methods TKIP (Temporal Key Integ-
rity Protocol) and AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) are available
for the encryption of data.
Proceed as follows:
1. Start the Printserver Homepage.
2. Click Configuration – Wireless.
3. Configure the WLAN parameters; see: Table 9
49
.
4. Click Save to confirm.
The settings are saved.
If the print server changes the network, it may receive a new IP con-
figuration. In that case, the connection to the Printserver Homepage
will be interrupted.
Table 9: WLAN Parameters
Parameters Description
Mode
Communication mode)
Defines the communication mode. The communication
mode defines the network structure in which the print
server will be installed. Two modes are available:
- In the 'ad-Hoc' mode, the print server communicates
directly with another WLAN client (peer-to-peer).
The 'infrastructure' mode is suitable for setting up large
wireless networks with several devices in different
rooms. Communication between the devices is done via
an access point which is connected to the network. The
access point can be protected by encryption or
authentication.
Network Settings
Print Server User Manual Windows 50
Network name
(SSID)
Defines the SSID. The ID of a wireless network is
referred to as SSID (Service Set Identifier) or network
name. Each wireless LAN has a configurable SSID in
order to clearly identify the wireless network. The SSID is
configured in the access point of a Wireless LAN. Each
device (PC, print server, etc.) that is intended to have
access to the wireless network must be configured using
the same SSID.
Channel
Frequency range)
Defines the channel (frequency range) on which the
entire data communication will be transmitted. The
product uses the 2.4 GHz ISM band. A channel has a
bandwidth of 22 MHz. The distance between two
neighboring channels is 5 MHz. Channel 3 is preset. The
parameter 'Channel' can only be configured in the 'Ad-
Hoc' mode.
Neighboring channels overlap, which can lead to
interferences. If several WLANs are operated in a small
radius, a distance of at least five channels should exist
between two channels.
Keep yourself informed about national provisions
regarding the use of WLAN products and only use
authorized channels.
Roaming Enables/disables the use of roaming. Roaming refers to
the 'moving' of one radio cell to the next. The print server
will use the access point that has the strongest signal. If
the print server moves towards the sphere of another
access point, the print server switches automatically and
without loss of connection to the next radio cell. The
parameter 'Roaming' can only be configured in the
'Infrastructure' mode.
-dBm Defines the roaming threshold in -dbm. If the WLAN
signal strength exceeds the threshold, the print server
searches for a stronger WLAN signal and may switch
into a WLAN with better signal strength. The value 65 -
dbm is preset. This parameter can only be configured in
the 'Infrastructure' mode.
Encryption method see: ’WLAN Security’ 48
Authentication method see: ’Netzwerkauthentifizierung’ 104
Parameters Description

Print Jobs and Print Data
Print Server User Manual Windows 72
Example The string 'white' is to be replaced by the string 'black' and the
string 'cat' is to be replaced by 'dog' in the print data.
Filter Function 'Job Start and Job End'
The print server allows the sending of start and end sequences
before/after a print job. These sequences may consist of PRESCRIBE
or ESC commands that trigger a form feed after the print job.
ESC commands consist of job start sequence '\027' followed by the
actual control characters preceded by a backslash and written as a
decimal. Job end sequence '\027 \012', for example, triggers a form
feed after the print job. For more information, please look up the
available ESC commands in your printer manual.
Configuration is done via logical printers, see: 73.
8.4 How to Convert Print Data
The print server offers many filters in order to convert print data.
Filter Function 'ASCII / PostScript'
The print server supports the conversion of print data from ASCII to
PostScript format. Configuration is done via logical printers, see:
73.
Filter Function 'HEX Dump Mode' (Hexadecimal + ASCII)
The print server supports the hex dump mode. The hex dump mode
is used to search for errors in print data in order to detect communi-
cation problems between the computer and the printer.
The hex dump mode displays each character both as hexadecimal
code and ASCII character code. Printer control commands are
printed as hexadecimal values and do not influence the printout in
any way. Configuration is done via logical printers, see: 73.
ASCII Decimal Hexadecimal
Search white;;cat \119\104\105\116\101;;\099\097\116 77 68 69 74 65 63 61 74
Replace black;;dog \098\108\097\099\107;;\100\111\103 62 6C 61 63 6B 64 6F 67
Produktspezifikationen
| Marke: | SEH |
| Kategorie: | Druckserver |
| Modell: | PS105 |
| Prozessortaktfrequenz: | 60 MHz |
| Gewicht: | 80 g |
| Betriebstemperatur: | 5 - 40 °C |
| Relative Luftfeuchtigkeit in Betrieb: | 20 - 80 % |
| Netzstandard: | IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3u |
| Unterstützte Sicherheitsalgorithmen: | 802.1x RADIUS, EAP, HTTPS |
| Zertifizierung: | CE, FCC, VCCI, WEEE, RoHS, C-Tick |
| Anzahl Ethernet-LAN-Anschlüsse (RJ-45): | 1 |
| Energiebedarf: | 100 - 240V |
| Schnittstelle: | RJ-45, IEEE1284B |
| Prozessor: | RISC |
| Management-Protokolle: | Raw TCP, LPR/LPD, IPP v1.1, AppleTalk, HTTP, FTP, NetBIOS, Novell iPrint (LPR/IPP), NDPS(IP/IPX), R/N, POP3, Bonjour, KonicaMinolta GDI |
| Kompatible Betriebssysteme: | Windows 95\nWindows 98\nWindows Me\nWindows NT 3.x\nWindows NT 4.x\nWindows XP\nWindows 2003 Server\nWindows 2008 Server\nWindows Vista\nWindows 7\nMac OS 7.x\nMAC OS 8.x\nMAC OS 9.x\nMAC OS 10.x\nNetWare 3.x\nNetWare 4.x\nNetWare 5.x\nNetWare 6.x\nLinux |
| Abmessungen (BxTxH): | 63 x 98 x 26 mm |
| Speicherkapazität: | 16 MB |
| Nachhaltigkeitszertifikate: | ENERGY STAR |
| Verkabelungstechnologie: | 10/100BASE-T(X) |
| Flash-Speicher: | 4 MB |
| Datenübertragungsrate: | 100 Mbit/s |
| Datenrate: | 10Mbit/s |
| Netzwerkfunktionen: | Schnelles Ethernet |
| Network Connection Typ: | Ethernet-LAN |
| IPP Unterstützung: | Ja |
Brauchst du Hilfe?
Wenn Sie Hilfe mit SEH PS105 benötigen, stellen Sie unten eine Frage und andere Benutzer werden Ihnen antworten
Bedienungsanleitung Druckserver SEH

13 August 2024

12 August 2024

12 August 2024

9 August 2024

8 August 2024

7 August 2024

22 April 2024

22 März 2024

20 Februar 2024

12 Februar 2024
Bedienungsanleitung Druckserver
- Druckserver Gembird
- Druckserver HP
- Druckserver Netgear
- Druckserver König
- Druckserver Lindy
- Druckserver TRENDnet
- Druckserver Dymo
- Druckserver TP-Link
- Druckserver Edimax
- Druckserver D-Link
- Druckserver Lexmark
- Druckserver Star
- Druckserver Digitus
- Druckserver LevelOne
- Druckserver Intellinet
- Druckserver Sitecom
- Druckserver Iogear
- Druckserver StarTech.com
- Druckserver AirLive
- Druckserver Atlantis Land
- Druckserver Hamlet
- Druckserver Silex
- Druckserver EXSYS
- Druckserver Hawking Technologies
- Druckserver Inter-Tech
- Druckserver Lantronix
Neueste Bedienungsanleitung für -Kategorien-

28 September 2024

24 September 2024

18 September 2024

18 September 2024

14 September 2024

6 September 2024

3 September 2024

1 September 2024

1 September 2024

1 September 2024